Here’s a detailed guide:
Primary Management Steps for Syncope
Stop Dental Procedure: Immediately stop any ongoing dental procedure.
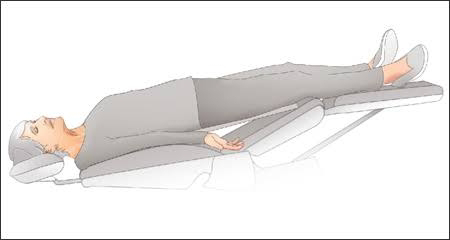
Positioning:
Supine Position: Lay the patient flat on their back.
Leg Elevation: Elevate the legs slightly (Trendelenburg position) to promote blood flow to the brain.
Airway Management:Ensure the airway is open and unobstructed.Loosen any tight clothing around the neck and chest.
Monitor Vital Signs:Check pulse, blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
Emergency Drugs for Syncope
Ammonia Inhalants:
Use: To arouse consciousness through inhalation.
Administration: Hold under the patient’s nose briefly.
Oxygen:
Use: To improve oxygenation.
Administration: Via nasal cannula or face mask at 4-6 liters per minute.
Atropine:
Use: For significant bradycardia (slow heart rate).
Dosage: 0.5 mg intravenously (IV), repeated every 3-5 minutes as needed, up to 3 mg total.
Epinephrine (Adrenaline):
Use: Primarily for anaphylaxis or severe hypotension, not typically for syncope.
Dosage: 0.3-0.5 mg intramuscularly (IM) using an auto-injector.
Glucose (Oral or IV):
Use: For hypoglycemia if suspected.
Administration: Oral glucose gel or 50% dextrose IV.
Supportive Measures
Vital Signs Monitoring:
Continuously monitor the patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
Comfort and Reassurance:
Reassure the patient and keep them calm.
Hydration and Nutrition:
Offer a sugary drink or snack once the patient is conscious and stable, if no contraindications exist.
Equipment Checklist
Oxygen delivery system (nasal cannula or mask)
Blood pressure monitor
Pulse oximeter
Emergency drug kit
Ammonia inhalants
Glucose gel or IV dextrose